Photoelectron spectroscopy ap chemistry
Photoelectron Spectroscopy Ap Chemistry. Photoelectron spectroscopy (you have the pogil) kj/mol now mj/mol the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gaseous state is defined as ionization energy and the energy required to remove the least tightly held electron is the first ionization energy. Practice interpreting photoelectron spectroscopy data in this set of free questions designed for ap chemistry students. Photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) is a lab technique that involves shooting an intense beam of radiation at a sample of an element and measuring the energy of the electrons that are ejected from. For the purposes of ap chemistry, we will only be considering the atoms of one element at a time.
 Photoelectron Spectroscopy Worksheet Answers Promotiontablecovers From promotiontablecovers.blogspot.com
Photoelectron Spectroscopy Worksheet Answers Promotiontablecovers From promotiontablecovers.blogspot.com
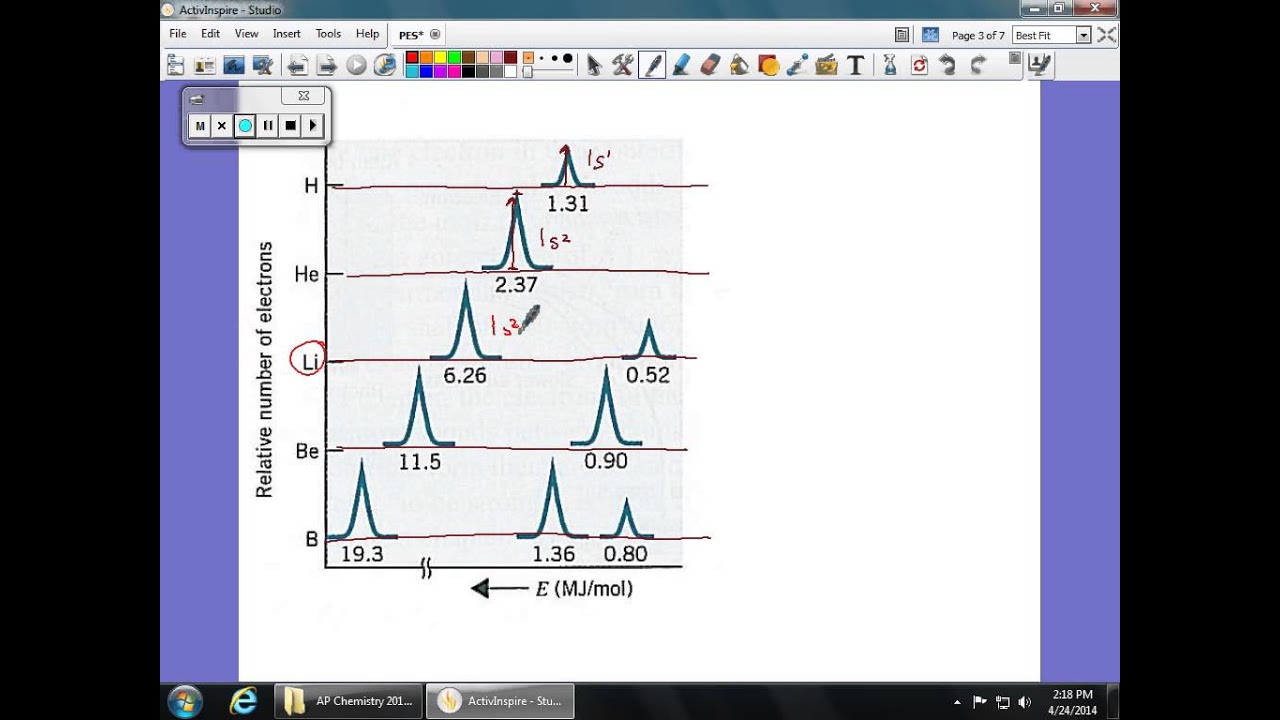
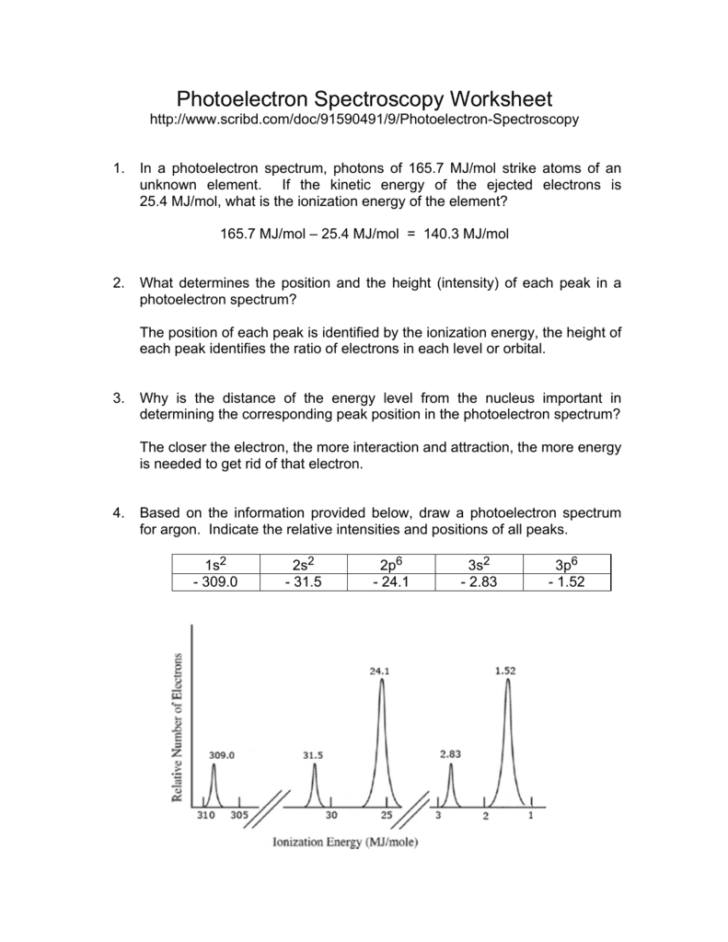
Why is there one peak in fluorine that is so much taller than all the others? For the purposes of ap chemistry, we will only be considering the atoms of one element at a time. Remember coulomb’s law f coulomb 𝝰 q 1 q 2 / r2. Since the 2p peak is twice the intensity of the 2s or 1 s peak, it has twice the electrons (4). Using the plot, write the electron configuration of the element, and identify it. First of all, the biggest thing you need to know how to do, regarding pes, is read the graph.
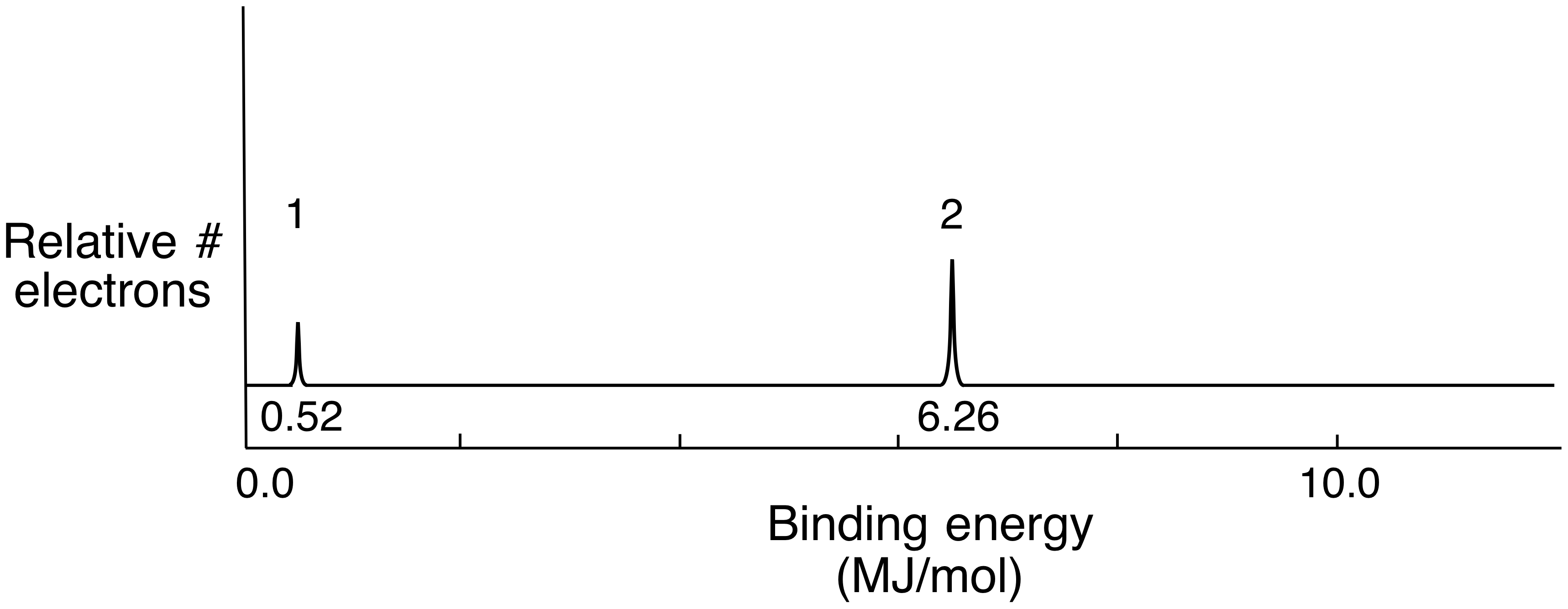
The next orbital has to be 2s and the pes indicates there are 2 electrons in this orbital.
The first orbital, as always, has to be 1s. Photoelectron spectroscopy (you have the pogil) kj/mol now mj/mol the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gaseous state is defined as ionization energy and the energy required to remove the least tightly held electron is the first ionization energy. 5) below is shown the pes spectrum. Why are the fluorine peaks to the left of the boron peaks? Exploring atomic structure using photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) data with jamie benigna Using the plot, write the electron configuration of the element, and identify it.
 Source: schoolbag.info
Source: schoolbag.info
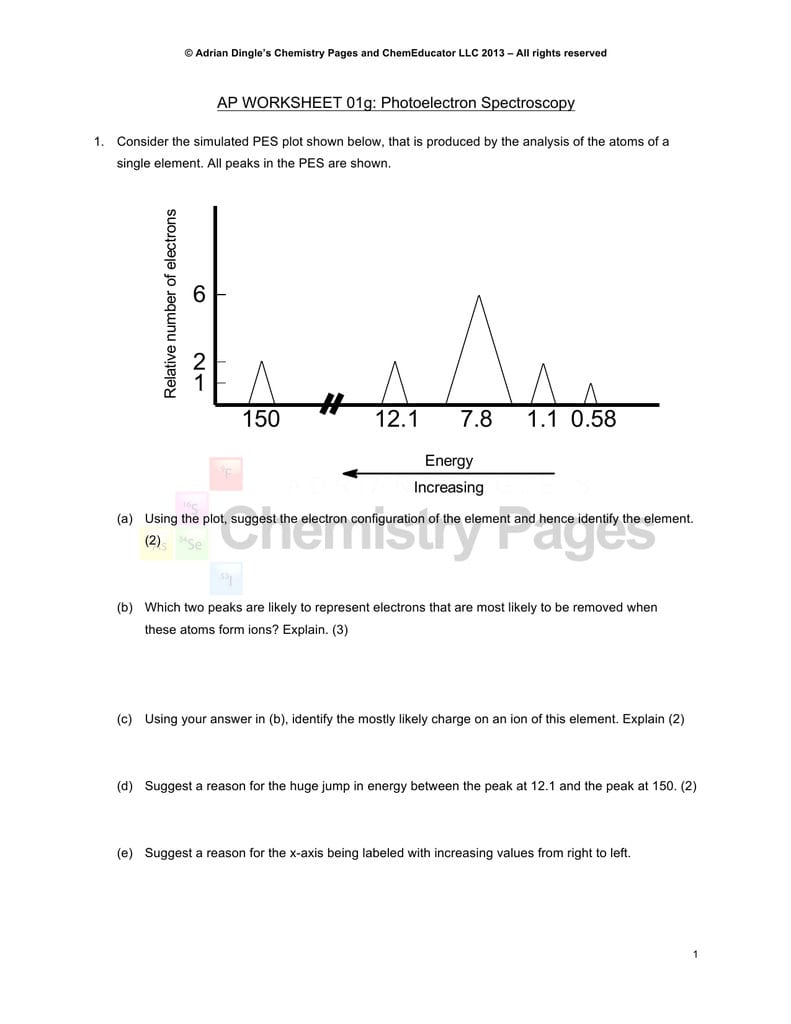
Consider the following pes spectrum a. Since the graph goes up to 2, there are 2 electrons in the 1s orbital. In photoelectron spectroscopy (pes), one can determine the identity of a substance by measuring the amount of energy needed to remove electrons from the substance’s component electrons. Using the plot, write the electron configuration of the element, and identify it. This guide will require you to be more diligent and memorize a table.
 Source: db-excel.com
Source: db-excel.com
The first orbital, as always, has to be 1s. The first orbital, as always, has to be 1s. Using the plot, write the electron configuration of the element, and identify it. This guide will require you to be more diligent and memorize a table. Ap chemistry free response question for electron spectroscopy.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Electrons that were originally further away from the nucleus require less energy to eject, and thus will be moving. So far, the electron configuration seems to be 1s^2 2s^2. Practice interpreting photoelectron spectroscopy data in this set of free questions designed for ap chemistry students. Electrons that were originally further away from the nucleus require less energy to eject, and thus will be moving. Ap chemistry free response question for electron spectroscopy.
 Source: fdocuments.in
Source: fdocuments.in
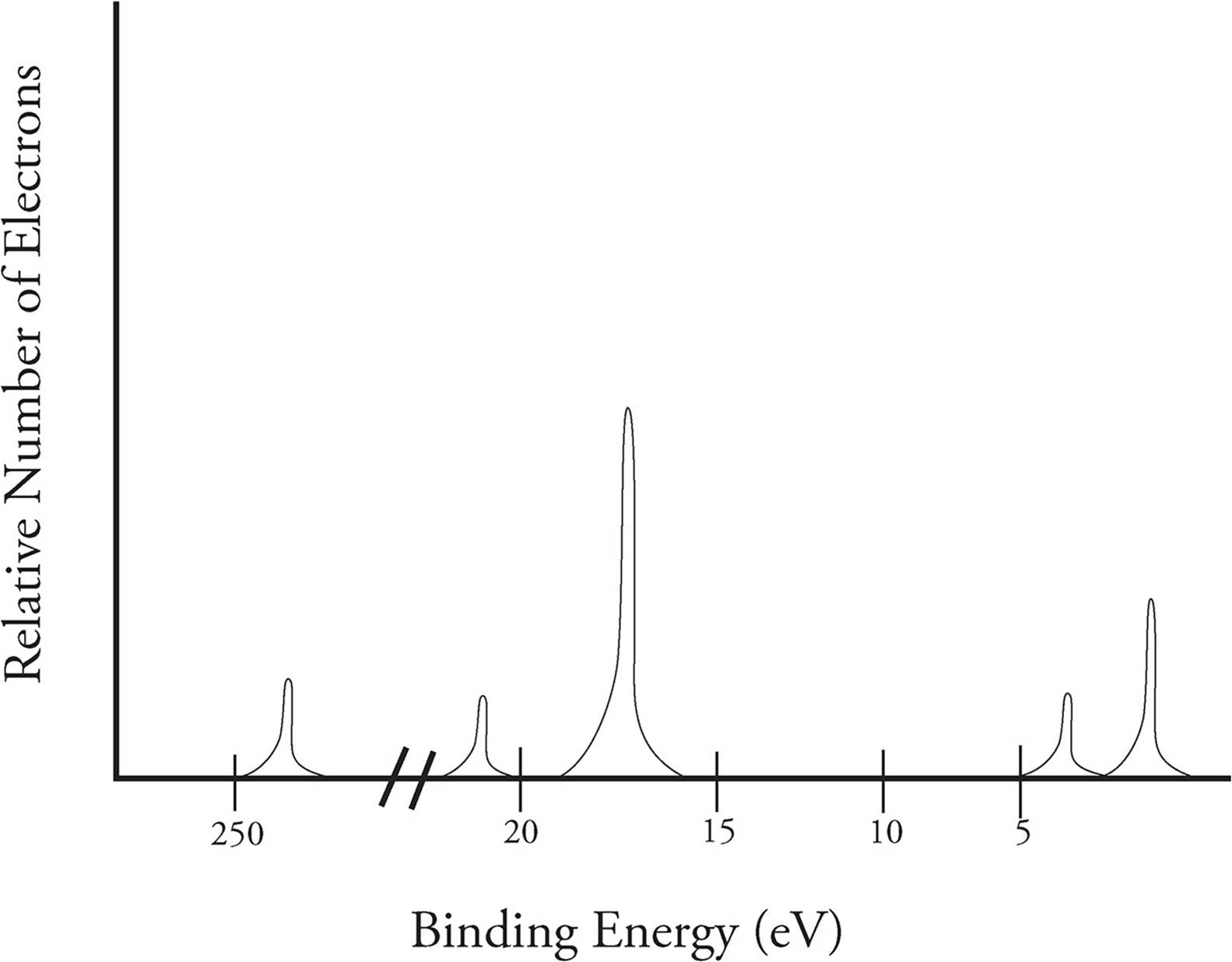
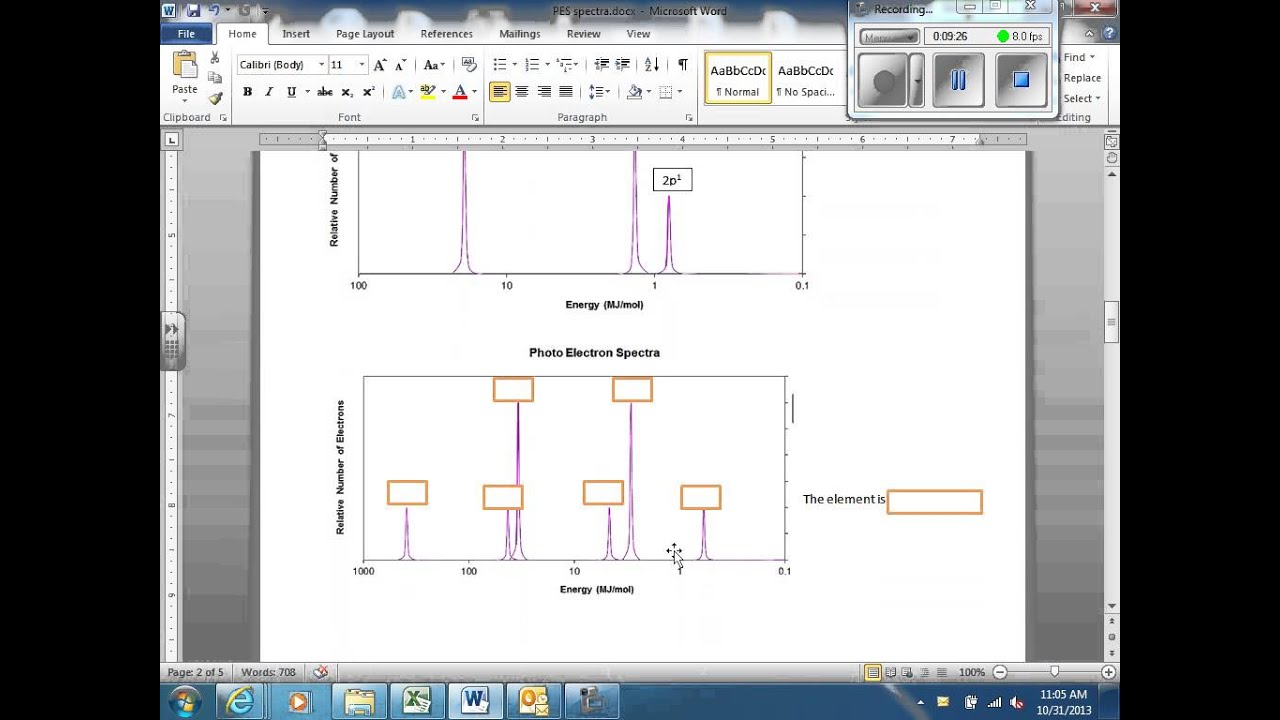
B) a student claims that the 1s peak for sulfur (s) would be further to the right than the 1s peak of this element. Consider the following photoelectron spectroscopy data: The next orbital has to be 2s and the pes indicates there are 2 electrons in this orbital. This video provides an in depth look at the concept of photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) and how to interpret the resulting spectrums. The peaks at lower energy would correspond to the 2s and 2p, respectively.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The first orbital, as always, has to be 1s. So far, the electron configuration seems to be 1s^2 2s^2. Ap chemistry notes and study guide photoelectron spectroscopy 1.6 (continued) incoming radiation = binding energy + kinetic energy (of the ejected electron) the faster an ejected electron is going the more kinetic energy it has. Suggest a reason for the huge jump in energy between peak a and peak b. Using the plot, write the electron configuration of the element, and identify it.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Exploring atomic structure using photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) data with jamie benigna Using the plot, write the electron configuration of the element, and identify it. Photoelectron spectroscopy (you have the pogil) kj/mol now mj/mol the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gaseous state is defined as ionization energy and the energy required to remove the least tightly held electron is the first ionization energy. First of all, the biggest thing you need to know how to do, regarding pes, is read the graph. Consider the following pes spectrum a.
 Source: promotiontablecovers.blogspot.com
Source: promotiontablecovers.blogspot.com
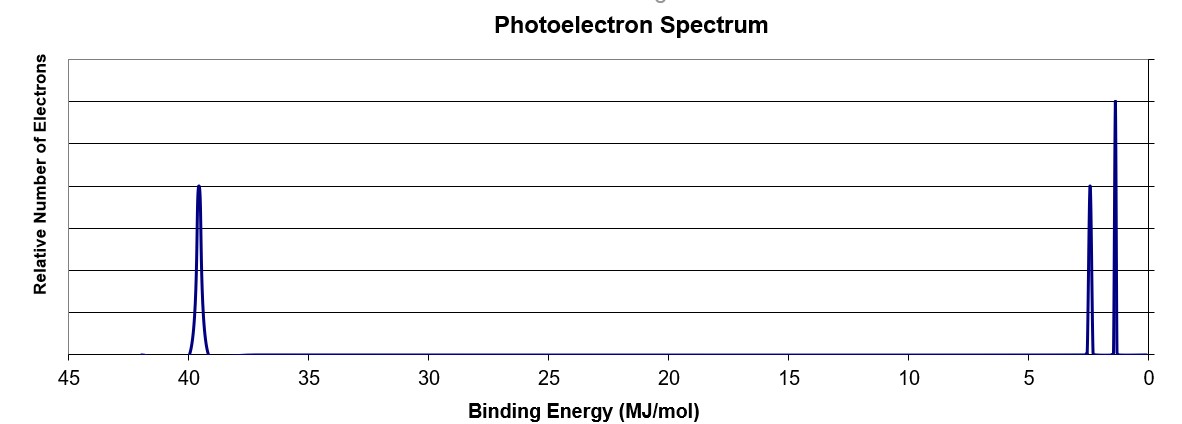
Scientists can infer particularly about the constituents of a substance as well as the bonds between the atoms in the material using this data. The peaks at lower energy would correspond to the 2s and 2p, respectively. The binding energy at ~ 53 mj represents the 1s orbital. Suggest a reason for the huge jump in energy between peak a and peak b. A) based on the graph, identify the element and write the full electron configuration.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Ap chemistry free response question for electron spectroscopy. The binding energy at ~ 53 mj represents the 1s orbital. Remember coulomb’s law f coulomb 𝝰 q 1 q 2 / r2. Since the 2p peak is twice the intensity of the 2s or 1 s peak, it has twice the electrons (4). This topic has been included in the redesigned ap® chemistry course, and may not be well understood by students.
 Source: varsitytutors.com
Source: varsitytutors.com
Otherwise, this will be rather short. Ap chemistry free response question for electron spectroscopy. Photoelectron spectroscopy (you have the pogil) kj/mol now mj/mol the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gaseous state is defined as ionization energy and the energy required to remove the least tightly held electron is the first ionization energy. Consider the following photoelectron spectroscopy data: 5) below is shown the pes spectrum.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
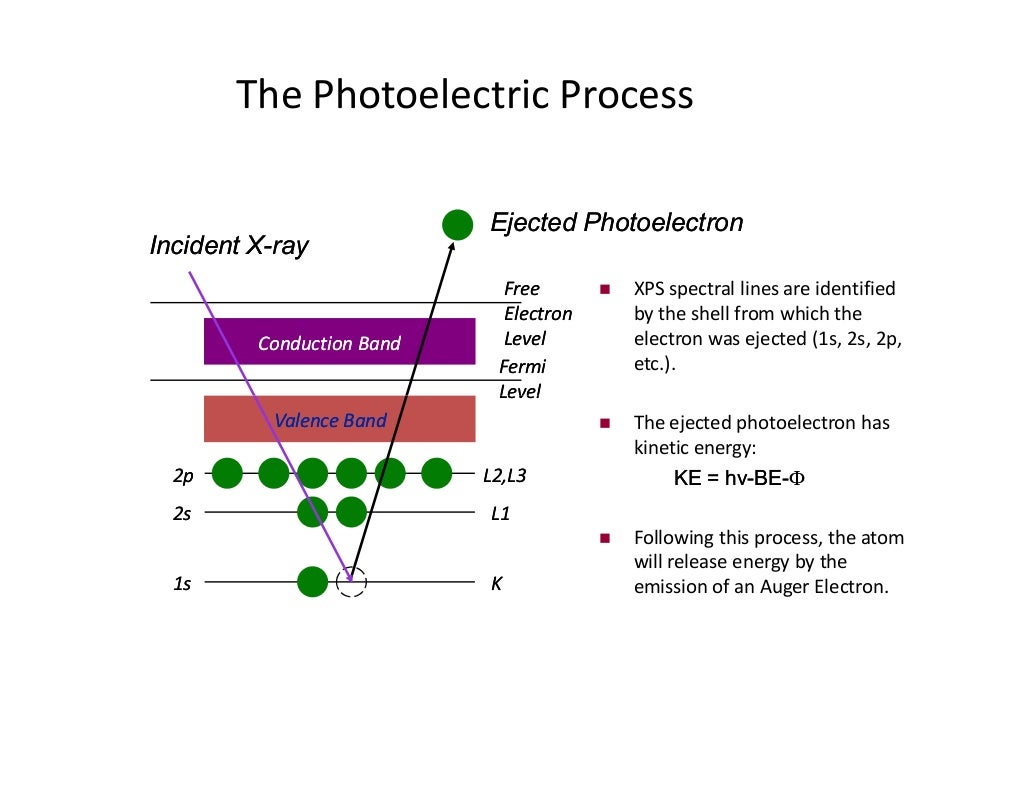
Since the 2p peak is twice the intensity of the 2s or 1 s peak, it has twice the electrons (4). Ap e 1 e p 00 page 45 e pee explaining relationships coulomb�s law can again be used to explain some aspects of photoelectron spectroscopy. Ap chemistry notes and study guide photoelectron spectroscopy 1.6 (continued) incoming radiation = binding energy + kinetic energy (of the ejected electron) the faster an ejected electron is going the more kinetic energy it has. Label each peak with the appropriate shell and subshell. Remember coulomb’s law f coulomb 𝝰 q 1 q 2 / r2.
 Source: fdocuments.in
Source: fdocuments.in
The binding energy at ~ 53 mj represents the 1s orbital. A) based on the graph, identify the element and write the full electron configuration. Why is there one peak in fluorine that is so much taller than all the others? Using the plot, write the electron configuration of the element, and identify it. Photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) is a lab technique that involves shooting an intense beam of radiation at a sample of an element and measuring the energy of the electrons that are ejected from.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Suggest a reason for the huge jump in energy between peak a and peak b. This guide will require you to be more diligent and memorize a table. Practice interpreting photoelectron spectroscopy data in this set of free questions designed for ap chemistry students. Electrons that were originally further away from the nucleus require less energy to eject, and thus will be moving. With other peaks present, this 1s orbital is fully occupied by 2 electrons.
 Source: db-excel.com
Source: db-excel.com
So far, the electron configuration seems to be 1s^2 2s^2. B) a student claims that the 1s peak for sulfur (s) would be further to the right than the 1s peak of this element. The next orbital has to be 2s and the pes indicates there are 2 electrons in this orbital. This video provides an in depth look at the concept of photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) and how to interpret the resulting spectrums. So far, the electron configuration seems to be 1s^2 2s^2.
 Source: fdocuments.in
Source: fdocuments.in
The peaks at lower energy would correspond to the 2s and 2p, respectively. Practice interpreting photoelectron spectroscopy data in this set of free questions designed for ap chemistry students. Ap chemistry free response question for electron spectroscopy. Electrons that were originally further away from the nucleus require less energy to eject, and thus will be moving. This topic has been included in the redesigned ap® chemistry course, and may not be well understood by students.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Photoelectron spectroscopy (you have the pogil) kj/mol now mj/mol the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gaseous state is defined as ionization energy and the energy required to remove the least tightly held electron is the first ionization energy. The binding energy at ~ 53 mj represents the 1s orbital. 1.5 photoelectron spectroscopy & electron configuration 3. First of all, the biggest thing you need to know how to do, regarding pes, is read the graph. This video provides an in depth look at the concept of photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) and how to interpret the resulting spectrums.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Suggest a reason for the huge jump in energy between peak a and peak b. Electrons that were originally further away from the nucleus require less energy to eject, and thus will be moving. Consider the following photoelectron spectroscopy data: The next orbital has to be 2s and the pes indicates there are 2 electrons in this orbital. Otherwise, this will be rather short.
 Source: chemedx.org
Source: chemedx.org
Since the graph goes up to 2, there are 2 electrons in the 1s orbital. Consider the following pes spectrum a. Since the 2p peak is twice the intensity of the 2s or 1 s peak, it has twice the electrons (4). This video provides an in depth look at the concept of photoelectron spectroscopy (pes) and how to interpret the resulting spectrums. B) a student claims that the 1s peak for sulfur (s) would be further to the right than the 1s peak of this element.
 Source: db-excel.com
Source: db-excel.com
Photoelectron spectroscopy is a useful technique for scientists because it allows them to explore the properties of matter (gases, solids, and liquids) by measuring electron orbital energies. B) a student claims that the 1s peak for sulfur (s) would be further to the right than the 1s peak of this element. Photoelectron spectroscopy is a useful technique for scientists because it allows them to explore the properties of matter (gases, solids, and liquids) by measuring electron orbital energies. For the purposes of ap chemistry, we will only be considering the atoms of one element at a time. This topic has been included in the redesigned ap® chemistry course, and may not be well understood by students.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title photoelectron spectroscopy ap chemistry by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.