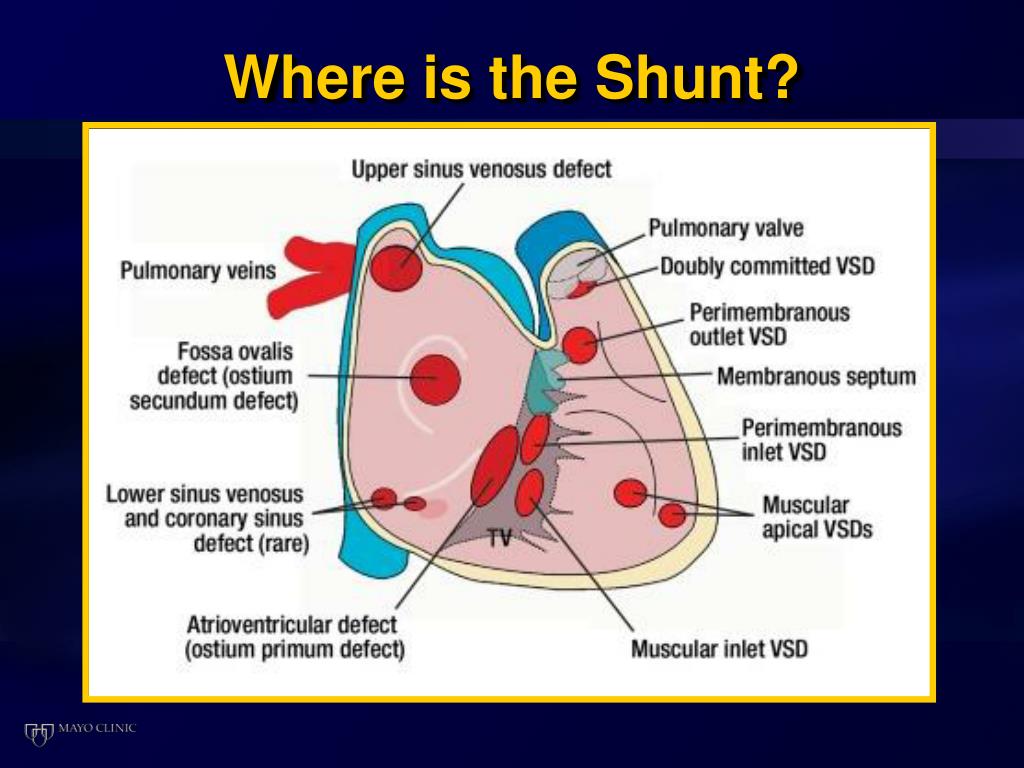
What is shunting in the lungs
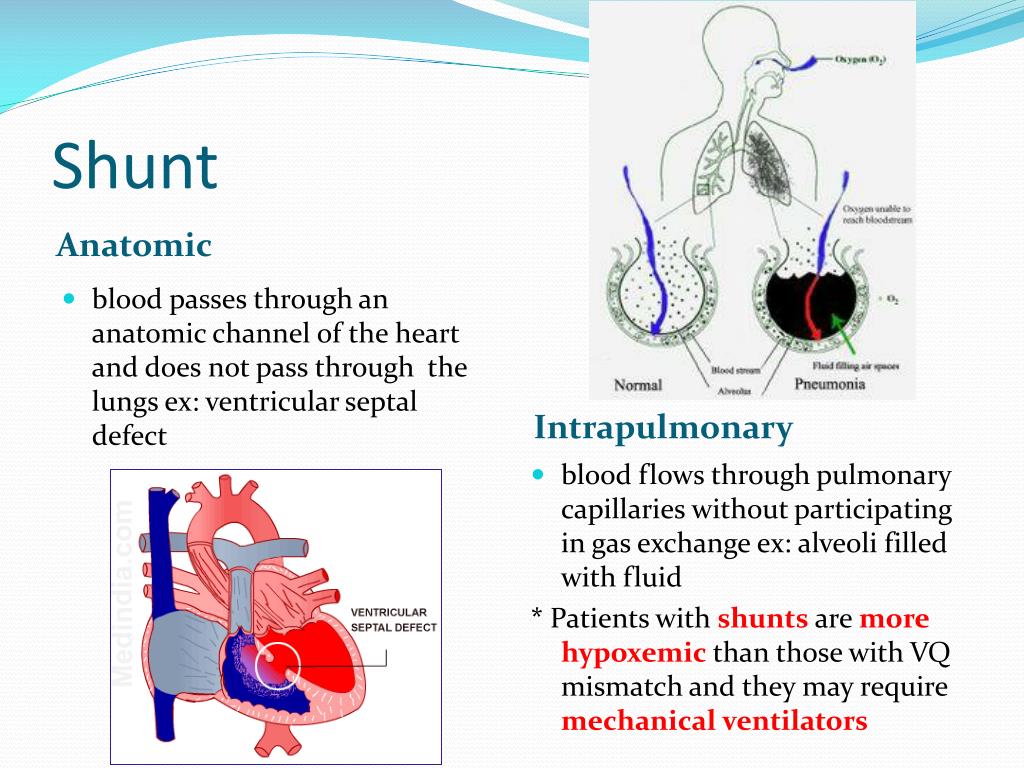
What Is Shunting In The Lungs. In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. Intrapulmonary shunting is the main cause of hypoxemia (inadequate blood oxygen) in pulmonary edema and conditions such as pneumonia in which the lungs become consolidated.the shunt fraction is the percentage of blood put out by the heart that is not completely oxygenated. Aetiology atelectasis, portal hypertension, small airway obstruction, smoke inhalation injury. It passes by the collapsed alveoli and is not able to complete the gas exchange.
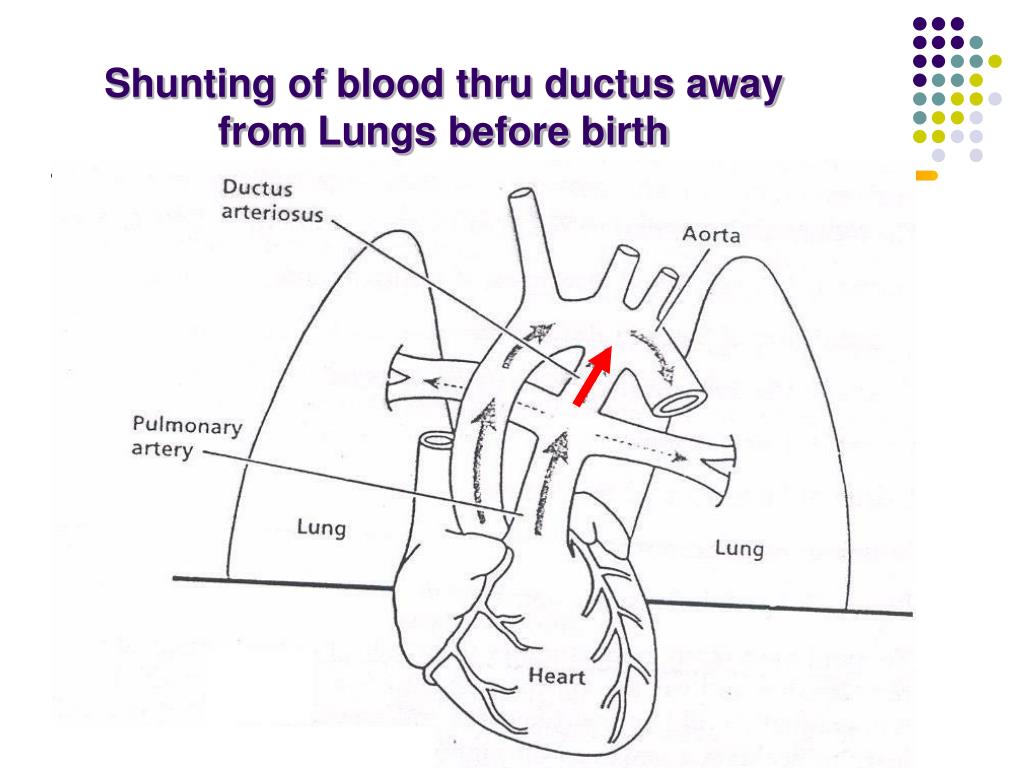 PPT Neonatal Resuscitation PowerPoint Presentation, free download From slideserve.com
PPT Neonatal Resuscitation PowerPoint Presentation, free download From slideserve.com
The pulmonary arteries divide into smaller arteries known as pulmonary. In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. Normally, lung tissue is thin and lacy but when fibrosis occurs, it’s like any scars on our body, there is a thickening of the tissue and a reduction in flexibility. Aetiology atelectasis, portal hypertension, small airway obstruction, smoke inhalation injury. What is shunting in the lungs. Diagnosis hypoxaemia that only partially improves with high inspired o2 concentrations (e.g., arterial o2 tension/pao2 < 200 mm hg for inspired o2 concentration fio2 = 100%).
Shunting of blood may result from abnormal vascular (blood vessel) communications or from blood flowing through unventilated portions of the lung (e.g., alveoli filled with fluid or inflammatory material).
This can cause problems for the patient as lack of oxygen will injure organs and tissues. Pulmonary shunting is blood that does not get any gas exchange at the alveolar level. What is shunting in the lungs. Shunting of blood may result from abnormal vascular (blood vessel) communications or from blood flowing through unventilated portions of the lung (e.g., alveoli filled with fluid or inflammatory material). Normally, lung tissue is thin and lacy but when fibrosis occurs, it’s like any scars on our body, there is a thickening of the tissue and a reduction in flexibility. It passes by the collapsed alveoli and is not able to complete the gas exchange.
 Source: thorax.bmj.com
Source: thorax.bmj.com
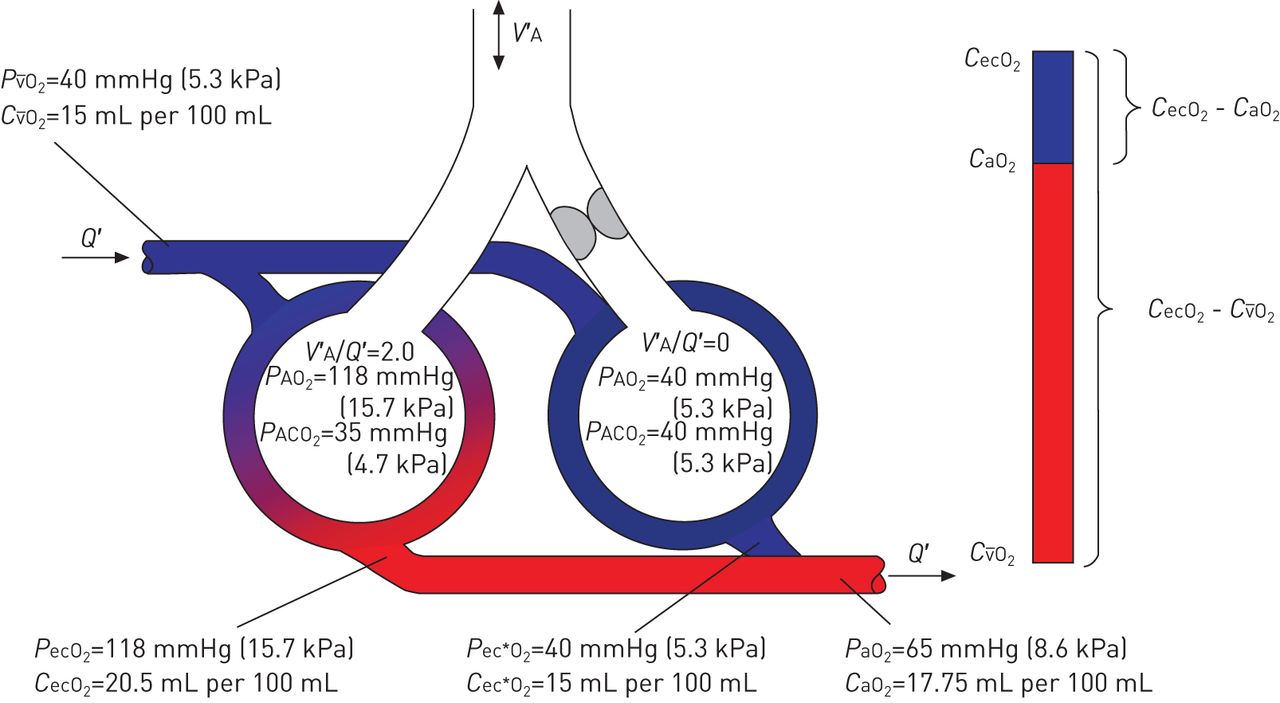
Q’t is the total pulmonary blood flow. What is shunting in the lungs. So, what causes shunting in the lungs? Shunt happens when venous and arterial blood mix and completely bypass the lungs (extrapulmonary shunt) or bypass the lungs without proper oxygenation (intrapulmonary shunt). In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue.
 Source: ctisus.com
Source: ctisus.com
Pulmonary shunt can be calculated by the following equation [figure 5]. Intrapulmonary shunt develops when blood passes through the lungs but fails to take part in gas exchange. Aetiology atelectasis, portal hypertension, small airway obstruction, smoke inhalation injury. The pulmonary arteries divide into smaller arteries known as pulmonary. Changing the locomotive of a trainattachingdetaching coaches or wagonschanging the order in which coaches.
 Source: doctorlib.info
Source: doctorlib.info
In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. Diagnosis hypoxaemia that only partially improves with high inspired o2 concentrations (e.g., arterial o2 tension/pao2 < 200 mm hg for inspired o2 concentration fio2 = 100%). Normally, lung tissue is thin and lacy but when fibrosis occurs, it’s like any scars on our body, there is a thickening of the tissue and a reduction in flexibility. The bypassing of alveoli by blood circulating through the lungs. Changing the locomotive of a trainattachingdetaching coaches or wagonschanging the order in which coaches.
 Source: osmosis.org
Source: osmosis.org
Pulmonary shunting is blood that does not get any gas exchange at the alveolar level. So, what causes shunting in the lungs? The pulmonary arteries divide into smaller arteries known as pulmonary. Shunt happens when venous and arterial blood mix and completely bypass the lungs (extrapulmonary shunt) or bypass the lungs without proper oxygenation (intrapulmonary shunt). This means when breathe, inhaling and exhaling, it’s harder for the tissue to expand and contract leading to less oxygen in our blood stream.
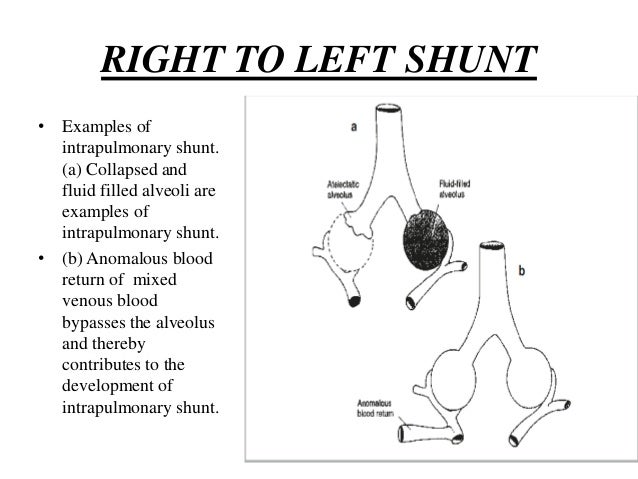 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
What is shunting in the lungs. In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. What is shunting in the lungs. We require more energy to breathe and the additional energy.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. Causes of shunt include pneumonia, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), alveolar collapse, and pulmonary arteriovenous communication. Aetiology atelectasis, portal hypertension, small airway obstruction, smoke inhalation injury. Diagnosis hypoxaemia that only partially improves with high inspired o2 concentrations (e.g., arterial o2 tension/pao2 < 200 mm hg for inspired o2 concentration fio2 = 100%). So, what causes shunting in the lungs?
Source: researchgate.net
We require more energy to breathe and the additional energy. Intrapulmonary shunt develops when blood passes through the lungs but fails to take part in gas exchange. What causes shunting in the lungs? This can cause problems for the patient as lack of oxygen will injure organs and tissues. This means when breathe, inhaling and exhaling, it’s harder for the tissue to expand and contract leading to less oxygen in our blood stream.
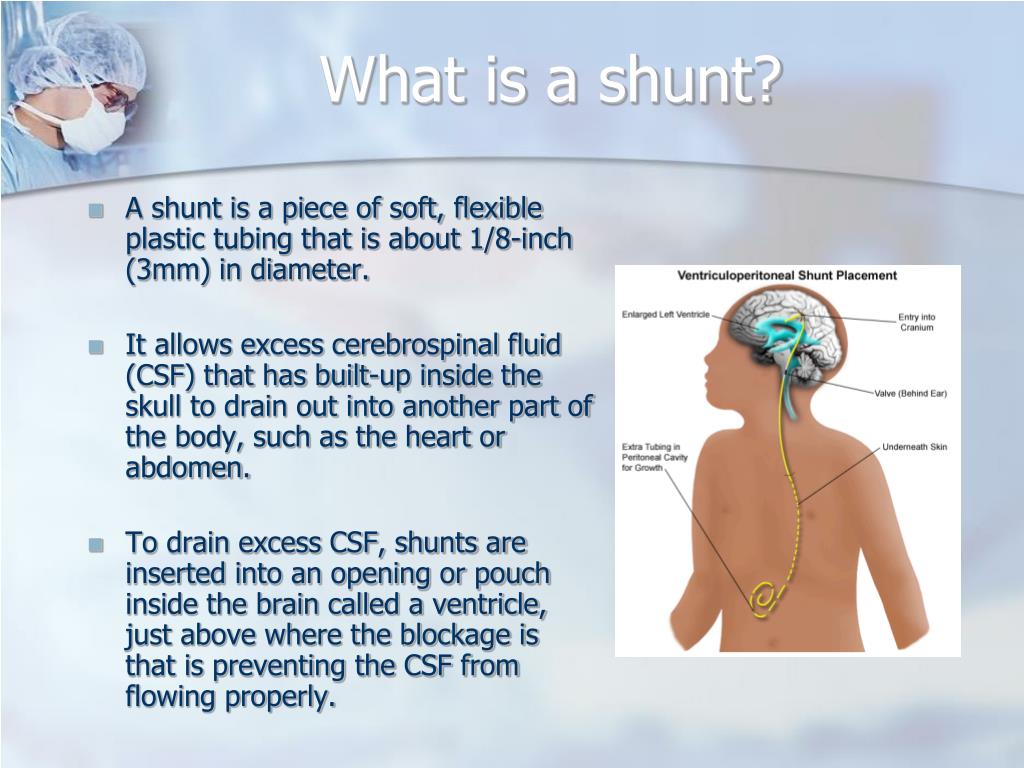 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Q’t is the total pulmonary blood flow. Pulmonary circulation starts with oxygen (o2) poor and carbon dioxide (co2) rich blood in the right atrium that flows into the right ventricle. So, what causes shunting in the lungs? Changing the locomotive of a trainattachingdetaching coaches or wagonschanging the order in which coaches. Shunting of blood may result from abnormal vascular (blood vessel) communications or from blood flowing through unventilated portions of the lung (e.g., alveoli filled with fluid or inflammatory material).
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Diagnosis hypoxaemia that only partially improves with high inspired o2 concentrations (e.g., arterial o2 tension/pao2 < 200 mm hg for inspired o2 concentration fio2 = 100%). Pulmonary circulation starts with oxygen (o2) poor and carbon dioxide (co2) rich blood in the right atrium that flows into the right ventricle. Shunting of blood may result from abnormal vascular (blood vessel) communications or from blood flowing through unventilated portions of the lung (e.g., alveoli filled with fluid or inflammatory material). It passes by the collapsed alveoli and is not able to complete the gas exchange. Causes of shunt include pneumonia, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), alveolar collapse, and pulmonary arteriovenous communication.
 Source: clipartbest.com
Source: clipartbest.com
Shunting of blood may result from abnormal vascular (blood vessel) communications or from blood flowing through unventilated portions of the lung (e.g., alveoli filled with fluid or inflammatory material). Normally, lung tissue is thin and lacy but when fibrosis occurs, it’s like any scars on our body, there is a thickening of the tissue and a reduction in flexibility. Shunt happens when venous and arterial blood mix and completely bypass the lungs (extrapulmonary shunt) or bypass the lungs without proper oxygenation (intrapulmonary shunt). Pulmonary shunting is blood that does not get any gas exchange at the alveolar level. Aetiology atelectasis, portal hypertension, small airway obstruction, smoke inhalation injury.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. Intrapulmonary shunt develops when blood passes through the lungs but fails to take part in gas exchange. What causes shunting in the lungs? In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. Shunt happens when venous and arterial blood mix and completely bypass the lungs (extrapulmonary shunt) or bypass the lungs without proper oxygenation (intrapulmonary shunt).
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Pulmonary circulation starts with oxygen (o2) poor and carbon dioxide (co2) rich blood in the right atrium that flows into the right ventricle. Changing the locomotive of a trainattachingdetaching coaches or wagonschanging the order in which coaches. Pulmonary circulation starts with oxygen (o2) poor and carbon dioxide (co2) rich blood in the right atrium that flows into the right ventricle. Almost all hypoxemia excluding changes in cardiac output in the hospital setting may be. Pulmonary shunting is blood that does not get any gas exchange at the alveolar level.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Intrapulmonary shunt develops when blood passes through the lungs but fails to take part in gas exchange. We require more energy to breathe and the additional energy. This means when breathe, inhaling and exhaling, it’s harder for the tissue to expand and contract leading to less oxygen in our blood stream. Q’t is the total pulmonary blood flow. Shunt happens when venous and arterial blood mix and completely bypass the lungs (extrapulmonary shunt) or bypass the lungs without proper oxygenation (intrapulmonary shunt).
 Source: airwayjedi.com
Source: airwayjedi.com
Causes of shunt include pneumonia, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), alveolar collapse, and pulmonary arteriovenous communication. Q’t is the total pulmonary blood flow. This means when breathe, inhaling and exhaling, it’s harder for the tissue to expand and contract leading to less oxygen in our blood stream. Normally, lung tissue is thin and lacy but when fibrosis occurs, it’s like any scars on our body, there is a thickening of the tissue and a reduction in flexibility. Intrapulmonary shunt develops when blood passes through the lungs but fails to take part in gas exchange.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Q’t is the total pulmonary blood flow. Shunting of blood may result from abnormal vascular (blood vessel) communications or from blood flowing through unventilated portions of the lung (e.g., alveoli filled with fluid or inflammatory material). This means when breathe, inhaling and exhaling, it’s harder for the tissue to expand and contract leading to less oxygen in our blood stream. The pulmonary arteries divide into smaller arteries known as pulmonary. What is shunting in the lungs.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
What is shunting in the lungs. Almost all hypoxemia excluding changes in cardiac output in the hospital setting may be. Intrapulmonary shunting is the main cause of hypoxemia (inadequate blood oxygen) in pulmonary edema and conditions such as pneumonia in which the lungs become consolidated.the shunt fraction is the percentage of blood put out by the heart that is not completely oxygenated. Shunt happens when venous and arterial blood mix and completely bypass the lungs (extrapulmonary shunt) or bypass the lungs without proper oxygenation (intrapulmonary shunt). We require more energy to breathe and the additional energy.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Almost all hypoxemia excluding changes in cardiac output in the hospital setting may be. Q’t is the total pulmonary blood flow. In shunting, venous blood enters the bloodstream without passing through functioning lung tissue. Almost all hypoxemia excluding changes in cardiac output in the hospital setting may be. Pulmonary shunting is blood that does not get any gas exchange at the alveolar level.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Shunting of blood may result from abnormal vascular (blood vessel) communications or from blood flowing through unventilated portions of the lung (e.g., alveoli filled with fluid or inflammatory material). Almost all hypoxemia excluding changes in cardiac output in the hospital setting may be. What is shunting in the lungs. Causes of shunt include pneumonia, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), alveolar collapse, and pulmonary arteriovenous communication. Pulmonary circulation starts with oxygen (o2) poor and carbon dioxide (co2) rich blood in the right atrium that flows into the right ventricle.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is shunting in the lungs by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






