Powdery mildew life cycle
Powdery Mildew Life Cycle. Powdery mildew life cycle and growth. Even though each species of powdery mildew attacks only a narrow range of hosts, there are 11,000 species of the powdery mildew fungi, and many ornamentals are hosts. Powdery mildew, plant disease of worldwide occurrence that causes a powdery growth on the surface of leaves, buds, young shoots, fruits, and flowers. Their biology and social impact
 Apple powdery mildew From apsnet.org
Apple powdery mildew From apsnet.org
The mycelium of powdery mildew on the leaf looks like a dry white powder. Knowledge of the life cycle of a powdery mildew fungus can provide important clues to epidemiology and disease control. Below is the powdery mildew life cycle, to help you get the maximum control, the best products from our range have been incorporated. Powdery mildew life cycle and wine grape infection information. Spores can be sexual or asexual depending on the type of fungus and the stage of its life cycle. Spores never stop producing more spores, so if infected leaves are not destroyed, the problem can never be.
For example, grapes infected with powdery mildew are not risk of infesting nearby strawberries.
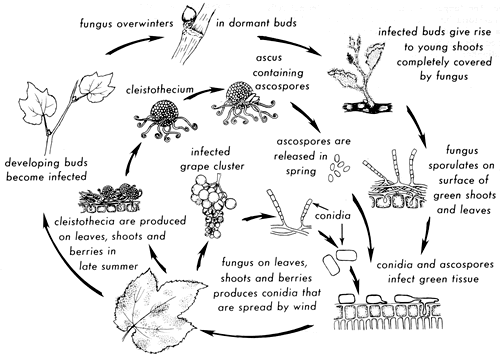
Life cycle of powdery mildew (diagram courtesy of nicholas, magarey and wachel, 1994, grape production series number 1: In spring, the infected buds break dormancy and the fungus resumes growth, colonizing the developing shoots and young leaf tissue. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of fungi in the order erysiphales. The name “powdery mildew” is a very descriptive and sums up the fungus’s appearance on the leaf surface very well. These are short hyphae which penetrate. They survive as ascospores or perithecia, structures containing ascospores.
 Source: pinterest.nz
Source: pinterest.nz
Powdery mildew fungi are obligate parasites (organisms that are totally dependent on a living host for its nutrients) and all but a few are ectoparasitic (living on the outside of the host). All the information you need about wine and winemaking. Below is the powdery mildew life cycle, to help you get the maximum control, the best products from our range have been incorporated. Their biology and social impact The mycelium of powdery mildew on the leaf looks like a dry white powder.
Source: enoviti-hanumangirl.blogspot.co.nz
Disease cycle of apple powdery mildew. Powdery mildew commonly winters over as mycelial mats in dormant buds or on plant stems and fallen. A complete life cycle includes both asexual and sexual reproduction. Hundreds of species of trees, shrubs, vines,. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems.
 Source: syngentaornamentals.co.ke
Source: syngentaornamentals.co.ke
Life cycle and appearance of powdery mildew. Spores can be sexual or asexual depending on the type of fungus and the stage of its life cycle. Plants in the field often do not become affected until after fruit initiation. Powdery mildew fungi are obligate parasites (organisms that are totally dependent on a living host for its nutrients) and all but a few are ectoparasitic (living on the outside of the host). Nearly 40% of the fungicide sprayed on roses is to control powdery mildew.
 Source: apsnet.org
Source: apsnet.org
Plants in the field often do not become affected until after fruit initiation. Knowledge of the life cycle of a powdery mildew fungus can provide important clues to epidemiology and disease control. Tritici february 2015 phytopathology 1056. Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Life cycle of powdery mildew image adapted from:
 Source: captionsmoreca.blogspot.com
Source: captionsmoreca.blogspot.com
Powdery mildew fungi are host specific, so they can only survive on their specific host plant, and there is no risk of cross contaminating different plant types. Powdery mildew fungi are obligate parasites (organisms that are totally dependent on a living host for its nutrients) and all but a few are ectoparasitic (living on the outside of the host). Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Life cycle of powdery mildew (diagram courtesy of nicholas, magarey and wachel, 1994, grape production series number 1: Shishkoff, in reference module in life sciences, 2017 abstract.
 Source: captionsmoreca.blogspot.com
Source: captionsmoreca.blogspot.com
New spores are carried on the wind to other parts of the plant or to other nearby plants. The sexual state includes the ascocarps (variously termed perithecia, cleistothecia, and chasmothecia. The disease can cause distortion and death of. Spores can be sexual or asexual depending on the type of fungus and the stage of its life cycle. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems.
 Source: syngentaornamentals.co.ke
Source: syngentaornamentals.co.ke
Even though each species of powdery mildew attacks only a narrow range of hosts, there are 11,000 species of the powdery mildew fungi, and many ornamentals are hosts. New insights into the life cycle of the wheat powdery mildew: Alternating between products with different points of application is important. Below is the powdery mildew life cycle to help you get the maximum control the best products from our range have been incorporated. Tritici february 2015 phytopathology 1056.
 Source: captionsmoreca.blogspot.com
Source: captionsmoreca.blogspot.com
In spring, the infected buds break dormancy and the fungus resumes growth, colonizing the developing shoots and young leaf tissue. Life cycle and appearance of powdery mildew. Spores never stop producing more spores, so if infected leaves are not destroyed, the problem can never be. All the information you need about wine and winemaking. Powdery mildew fungi are obligate parasites (organisms that are totally dependent on a living host for its nutrients) and all but a few are ectoparasitic (living on the outside of the host).
Source: enoviti-hanumangirl.blogspot.com
However, different powdery mildew species may be. Powdery mildew life cycle and wine grape infection information. They survive as ascospores or perithecia, structures containing ascospores. The mycelium of powdery mildew on the leaf looks like a dry white powder. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems.
 Source: blog.ucbmsh.org
Source: blog.ucbmsh.org
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. These are short hyphae which penetrate. Powdery mildew development is arrested when daytime temperatures are at least 100°f. Direct observation of ascosporic infection in blumeria graminis f. The asexual state produces conidia (asexual spores).
Source: encyclopedia.pub
The mycelium of powdery mildew on the leaf looks like a dry white powder. Powdery mildew fungi are host specific, so they can only survive on their specific host plant, and there is no risk of cross contaminating different plant types. Life cycle and appearance of powdery mildew. Direct observation of ascosporic infection in blumeria graminis f. Most fungi produce reproductive structures known as spores.
 Source: apsnet.org
Source: apsnet.org
Return to host infection page. Spores of powdery mildew overwinter on diseased plant parts and begin asexual production of new spores once the weather warms. However, different powdery mildew species may be. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Nearly 40% of the fungicide sprayed on roses is to control powdery mildew.
 Source: canr.msu.edu
However, different powdery mildew species may be. Direct observation of ascosporic infection in blumeria graminis f. Disease cycle of powdery mildew. New spores are carried on the wind to other parts of the plant or to other nearby plants. The fungi that cause powdery mildew (erysiphe, podosphaera, oïdium, leveillula) are all biotrophic fungi, meaning they feed on living plant cells and barely survive in the absence of a living crop.
 Source: canr.msu.edu
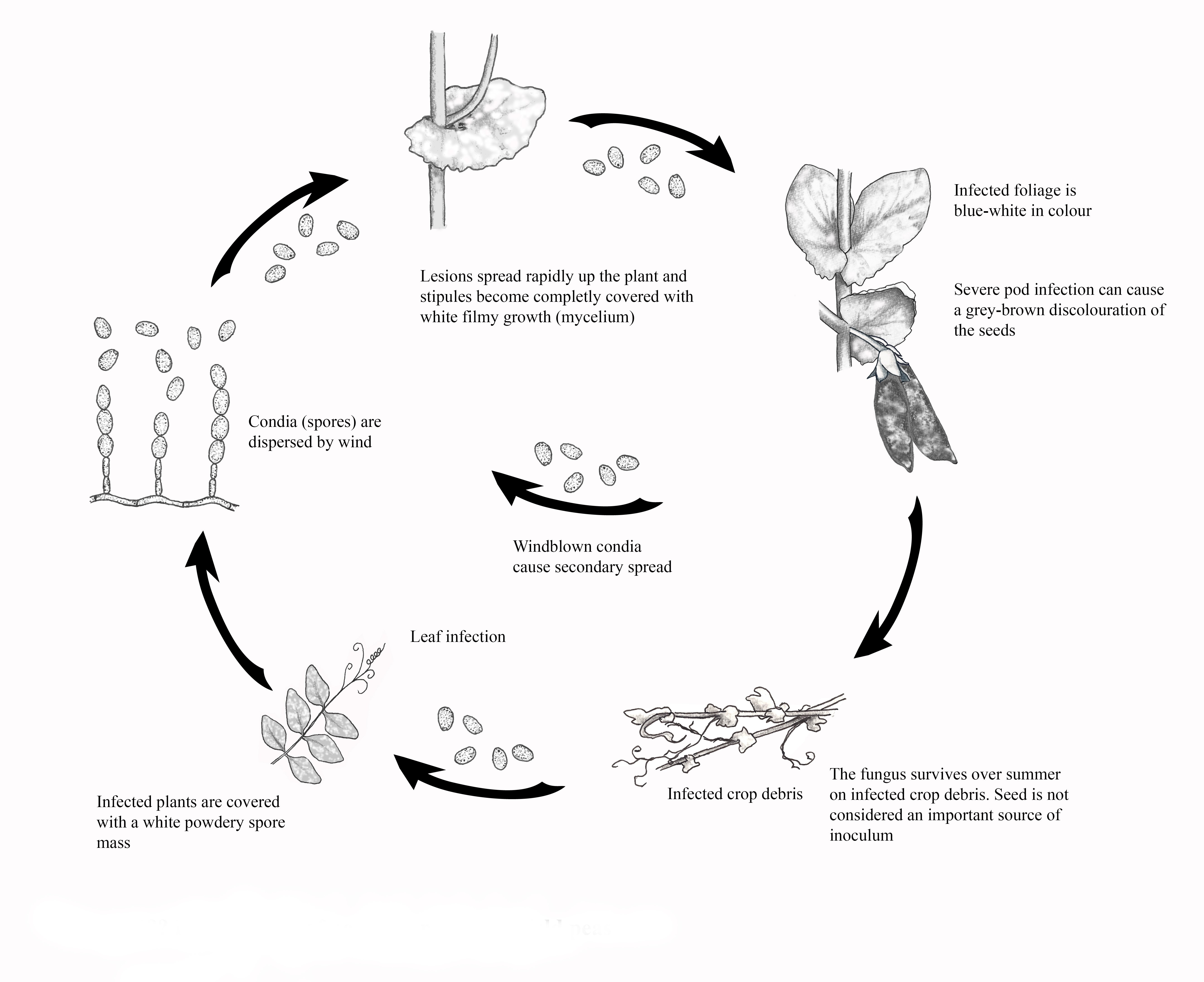
Disease cycle of powdery mildew. Spores can be sexual or asexual depending on the type of fungus and the stage of its life cycle. Leucotricha overwinters as mycelium in dormant flower and shoot buds infected the previous year. Life cycle of powdery mildew (diagram courtesy of nicholas, magarey and wachel, 1994, grape production series number 1: The fungi that cause powdery mildew (erysiphe, podosphaera, oïdium, leveillula) are all biotrophic fungi, meaning they feed on living plant cells and barely survive in the absence of a living crop.
 Source: evineyardapp.com
Source: evineyardapp.com
Although blumeria graminis is an intensively studied pathogen, an important part of its life cycle (namely, the way ascospores initiate primary infections on cereal leaves) has not yet been explored in detail. Powdery mildew commonly winters over as mycelial mats in dormant buds or on plant stems and fallen. The mycelium of powdery mildew on the leaf looks like a dry white powder. Spores never stop producing more spores, so if infected leaves are not destroyed, the problem can never be. Life cycle of powdery mildew (diagram courtesy of nicholas, magarey and wachel, 1994, grape production series number 1:
Source: apsnet.org
They survive as ascospores or perithecia, structures containing ascospores. The mycelium of powdery mildew on the leaf looks like a dry white powder. In spring, the infected buds break dormancy and the fungus resumes growth, colonizing the developing shoots and young leaf tissue. Heat if necessary and ensure adequate ventilation to inhibit the development of the disease. Life cycle of powdery mildew image adapted from:
 Source: extensionaus.com.au
Source: extensionaus.com.au
The mycelium of powdery mildew on the leaf looks like a dry white powder. Nearly 40% of the fungicide sprayed on roses is to control powdery mildew. They survive as ascospores or perithecia, structures containing ascospores. New spores are carried on the wind to other parts of the plant or to other nearby plants. Plants in the field often do not become affected until after fruit initiation.
 Source: agric.wa.gov.au
Leucotricha overwinters as mycelium in dormant flower and shoot buds infected the previous year. Heat if necessary and ensure adequate ventilation to inhibit the development of the disease. Powdery mildew life cycle and wine grape infection information. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of fungi in the order erysiphales. These are short hyphae which penetrate.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title powdery mildew life cycle by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





