Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology nursing
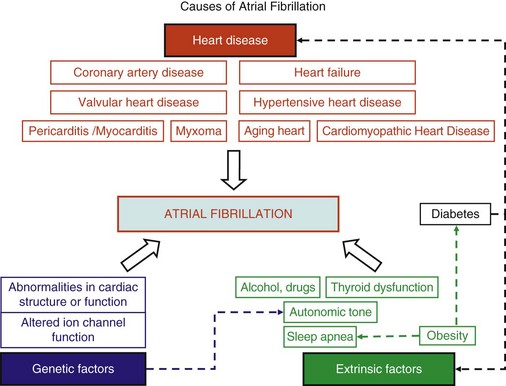
Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology Nursing. Atrial fibrillation (af) has strong associations with other cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure, coronary artery disease (cad), valvular heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. The medical team should be notified immediately if the patient’s heart rate is. Advanced age hypertension heart failure cardiomyopathy diabetes coronary heart disease rheumatic heart disease cardiothoracic surgery esophageal surgery history of stroke or transient ischemic attack alcohol and drug use genetic factors atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia seen in the clinical area. Patients can also have chronic afib, but.
 Pin on Nursing From pinterest.com
Pin on Nursing From pinterest.com
To enable better treatment and prevention of af a clearer understanding of the development and progression of atrial fibrillation is needed. Atrial fibrillation among older adults: The main goal of treatment is to maintain adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion and to ensure that the patient does not develop a thromboembolism. During atrial fibrillation, the heart�s upper chambers (the atria) beat chaotically and irregularly — out of sync with the lower chambers (the ventricles) of the heart. Nursing management of atrial fibrillation. Pharmacologic treatment includes selective beta 1 adrenergic receptor blockers to decreases the automaticity of contractions.
Atrial fibrillation (afib) can lead to heart failure, stroke, blood clots, and other complications of the heart.
The medical team should be notified immediately if the patient’s heart rate is. Atrial fibrillation (af) has strong associations with other cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure, coronary artery disease (cad), valvular heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. Pharmacologic treatment includes selective beta 1 adrenergic receptor blockers to decreases the automaticity of contractions. Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia among older adults. Risk for decreased cardiac output. Population, the incidence of atrial fibrillation is expected to double within the next 50 years.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The presence of afib increases a patient’s susceptibility to developing stroke, heart failure, and other cardiac issues. Patients can also have chronic afib, but. Ecg showing atrial fibrillation with fast ventricular tachycardia the pathophysiology of af has been studied extensively and is a subject of continuing research so that better preventive and curative therapies can be developed. An electrical activity disturbance in the heart that causes an irregular and often rapid heartbeat. Stanley nattel, md abstract—atrial fibrillation (af), the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, is an important contributor to population morbidity and mortality.
 Source: nursingexercise.com
Source: nursingexercise.com
Myocardial stretch, fibrosis, and chamber dilation all alter the electrical paths of the heart. Atrial fibrillation is something many acute care nurses will deal with, as it is a common complication after various surgeries. Atrial fibrillation (af) is common in patients with hf, and occurrence increases with hf severity (maisel et. By felice hefferan, msn, rn. The prevalence of atrial fibrillation (af), already the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, is constantly rising, even after adjusting for age and presence of structural heart disease.
 Source: pinterest.com.au
Source: pinterest.com.au
During atrial fibrillation, the heart�s upper chambers (the atria) beat chaotically and irregularly — out of sync with the lower chambers (the ventricles) of the heart. Advanced age hypertension heart failure cardiomyopathy diabetes coronary heart disease rheumatic heart disease cardiothoracic surgery esophageal surgery history of stroke or transient ischemic attack alcohol and drug use genetic factors atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia seen in the clinical area. Stanley nattel, md abstract—atrial fibrillation (af), the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, is an important contributor to population morbidity and mortality. Pharmacologic treatment includes selective beta 1 adrenergic receptor blockers to decreases the automaticity of contractions. View atrial fibrillation.docx from nursing misc at rutgers university, newark.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Myocardial stretch, fibrosis, and chamber dilation all alter the electrical paths of the heart. Dverse lifestyle, for example smoking, excess alcohol and unhealthy diet. The exact mechanisms by which cardiovascular risk. Indeed, atrial fibrillation is responsible for over 450,000 hospitalizations and 99,000 deaths annually and adds up to $26 billion to u.s. Seton hall university atrial fibrillation pathophysiology katherine lang professor rob church atrial fibrillation, or study resources
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The prevalence of atrial fibrillation (af), already the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, is constantly rising, even after adjusting for age and presence of structural heart disease. Dverse lifestyle, for example smoking, excess alcohol and unhealthy diet. In afib, the atria ( the hearts upper two chambers) beat irregularly and at a high rate. Atrial fibrillation results from rapid electrical activity that arises from different ectopic foci. The prevalence of atrial fibrillation has been increasing steadily and healthcare professionals need to be aware of the modifiable risk factors for developing af including:
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The main goal of treatment is to maintain adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion and to ensure that the patient does not develop a thromboembolism. The atria quiver sending confusing electrical signals to the ventricles, leaving them unsure of when to contract thus beating irregularly. The main goal of treatment is to maintain adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion and to ensure that the patient does not develop a thromboembolism. The prevalence of atrial fibrillation has been increasing steadily and healthcare professionals need to be aware of the modifiable risk factors for developing af including: By felice hefferan, msn, rn.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
To enable better treatment and prevention of af a clearer understanding of the development and progression of atrial fibrillation is needed. By felice hefferan, msn, rn. Given the aging of the u.s. There is evidence that nursing. The medical team should be notified immediately if the patient’s heart rate is.
 Source: bipboppingdays.blogspot.co.id
Source: bipboppingdays.blogspot.co.id
Valvular heart disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, aortic stenosis, hypertension, coronary artery disease, pericarditis, thyrotoxicosis, pulmonary disease, cardiac surgery, alcohol excess, and alcohol withdrawal are associated with atrial fibrillation. The main goal of treatment is to maintain adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion and to ensure that the patient does not develop a thromboembolism. Below are three (3) cardiac arrhythmia (digitalis toxicity) nursing care plans (ncp) and nursing diagnosis: Seton hall university atrial fibrillation pathophysiology katherine lang professor rob church atrial fibrillation, or study resources It is characterized by an irregular and often rapid heartbeat (see the first image below).
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Advanced age hypertension heart failure cardiomyopathy diabetes coronary heart disease rheumatic heart disease cardiothoracic surgery esophageal surgery history of stroke or transient ischemic attack alcohol and drug use genetic factors atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia seen in the clinical area. Indeed, atrial fibrillation is responsible for over 450,000 hospitalizations and 99,000 deaths annually and adds up to $26 billion to u.s. There is evidence that nursing. Nursing management of atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation occurs in three clinical circumstances:
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
View atrial fibrillation.docx from nursing misc at rutgers university, newark. Ecg showing atrial fibrillation with fast ventricular tachycardia the pathophysiology of af has been studied extensively and is a subject of continuing research so that better preventive and curative therapies can be developed. The medical team should be notified immediately if the patient’s heart rate is. Given the aging of the u.s. The presence of afib increases a patient’s susceptibility to developing stroke, heart failure, and other cardiac issues.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Atrial fibrillation, or afib, is a type of arrhythmia characterized by irregular and rapid heart rhythm that can lead to blood clot formation in the heart. Advanced age hypertension heart failure cardiomyopathy diabetes coronary heart disease rheumatic heart disease cardiothoracic surgery esophageal surgery history of stroke or transient ischemic attack alcohol and drug use genetic factors atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia seen in the clinical area. The medical team should be notified immediately if the patient’s heart rate is. Atrial fibrillation is something many acute care nurses will deal with, as it is a common complication after various surgeries. Given the aging of the u.s.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The medical team should be notified immediately if the patient’s heart rate is. Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia among older adults. Below are three (3) cardiac arrhythmia (digitalis toxicity) nursing care plans (ncp) and nursing diagnosis: Atrial fibrillation occurs in three clinical circumstances: Valvular heart disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, aortic stenosis, hypertension, coronary artery disease, pericarditis, thyrotoxicosis, pulmonary disease, cardiac surgery, alcohol excess, and alcohol withdrawal are associated with atrial fibrillation.
 Source: thoracickey.com
Source: thoracickey.com
View atrial fibrillation.docx from nursing misc at rutgers university, newark. In afib, the atria ( the hearts upper two chambers) beat irregularly and at a high rate. Atrial fibrillation, or afib, is a type of arrhythmia characterized by irregular and rapid heart rhythm that can lead to blood clot formation in the heart. Atrial fibrillation occurs in three clinical circumstances: Given the aging of the u.s.
 Source: nursestudy.net
Source: nursestudy.net
By felice hefferan, msn, rn. Atrial fibrillation occurs in three clinical circumstances: The main goal of treatment is to maintain adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion and to ensure that the patient does not develop a thromboembolism. Atrial fibrillation atrial fibrillation is described as a quivering or irregular and sometimes fast heart rate. Risk for decreased cardiac output.
 Source: etsy.com
Source: etsy.com
Risk for decreased cardiac output. Atrial fibrillation (af) has strong associations with other cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure, coronary artery disease (cad), valvular heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. By felice hefferan, msn, rn. The presence of afib increases a patient’s susceptibility to developing stroke, heart failure, and other cardiac issues. Atrial fibrillation atrial fibrillation is described as a quivering or irregular and sometimes fast heart rate.
 Source: pinterest.com.au
Source: pinterest.com.au
The main goal of treatment is to maintain adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion and to ensure that the patient does not develop a thromboembolism. Given the aging of the u.s. Indeed, atrial fibrillation is responsible for over 450,000 hospitalizations and 99,000 deaths annually and adds up to $26 billion to u.s. Nursing management of atrial fibrillation is an important skill for bedside nursing to master when caring for hospitalized patients. It is characterized by an irregular and often rapid heartbeat (see the first image below).
 Source: pinterest.se
Source: pinterest.se
Ecg showing atrial fibrillation with fast ventricular tachycardia the pathophysiology of af has been studied extensively and is a subject of continuing research so that better preventive and curative therapies can be developed. By felice hefferan, msn, rn. Nursing management of atrial fibrillation is an important skill for bedside nursing to master when caring for hospitalized patients. Classification pathophysiology and mechanisms of af. Myocardial stretch, fibrosis, and chamber dilation all alter the electrical paths of the heart.
 Source: healio.com
Source: healio.com
Health care costs each year. Indeed, atrial fibrillation is responsible for over 450,000 hospitalizations and 99,000 deaths annually and adds up to $26 billion to u.s. Stanley nattel, md abstract—atrial fibrillation (af), the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, is an important contributor to population morbidity and mortality. Atrial fibrillation (af) has strong associations with other cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure, coronary artery disease (cad), valvular heart disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. Atrial fibrillation is something many acute care nurses will deal with, as it is a common complication after various surgeries.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title atrial fibrillation pathophysiology nursing by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






